エルボ配管内の流れ (熱伝導)¶
シミュレーション名: flow__in_a_curved_pipe_XYZ3D
シミュレーション体系¶
エルボ配管内の流れを参考に
流入側の配管外側には、外径 300mm のヒーターを取り付けていた.
ヒータを 5 kW で加熱し、ヒータ→パイプ、及び、パイプ→水(静止)への熱伝導をみる.
パイプ、及び、水の初期温度は20℃ = 293.15 Kとした.
熱源としては、"Heat Source" keywordを用いて、重量密度あたりの熱源( 5.0e3 / 8.96e3 )を設定.
時間としては、10 (s) 毎に 50回の書き出しを実行する. ( Total = 500 (s) )
ヒータが熱が他に逃げる場所がないので、無限大に温度が上がっていってしまうが、ここでは無視する.
Elmer シミュレーションファイル¶
シミュレーションファイル ( heat.sif )を以下に示す.
heat.sif ( flow__in_acurved_pipe_XYZ3D )¶
include "./msh/model/mesh.names"
Header
CHECK KEYWORDS Warn
Mesh DB "." "msh/model"
Include Path ""
Results Directory "out/"
End
Simulation
Max Output Level = 3
Coordinate System = string "Cartesian"
Coordinate Mapping(3) = 1 2 3
Simulation Type = "Transient"
TimeStepping Method = BDF
BDF Order = 2
Timestep sizes(1) = 10.0
Timestep Intervals(1) = 50
Steady State Max Iterations = 10
End
Constants
Gravity(4) = 0 0 -1 9.82 !! m/s^2
End
Solver 1
Equation = "HeatEquations"
Procedure = "HeatSolve" "HeatSolver"
Variable = "Temperature"
Exec Solver = "Always"
Stabilize = True
Bubbles = False
Optimize Bandwidth = True
Steady State Convergence Tolerance = 1.0e-5
Nonlinear System Convergence Tolerance = 1.0e-3
Nonlinear System Max Iterations = 1
Nonlinear System Newton After Iterations = 3
Nonlinear System Newton After Tolerance = 1.0e-3
Nonlinear System Relaxation Factor = 1
Linear System Solver = Iterative
Linear System Iterative Method = BiCGStab
Linear System Max Iterations = 500
Linear System Convergence Tolerance = 1.0e-10
BiCGstabl polynomial degree = 2
Linear System Preconditioning = ILU0
Linear System ILUT Tolerance = 1.0e-3
Linear System Abort Not Converged = False
Linear System Residual Output = 20
Linear System Precondition Recompute = 1
End
Solver 2
Exec Solver = after saving
Equation = "Result output"
Procedure = "ResultOutputSolve" "ResultOutputSolver"
Output File Name = "heat"
Vtu Format = Logical True
Binary Output = Logical True
Scalar Field 1 = String temperature
End
Body 1
Name = "pipe"
Target Bodies(1) = $pipe
Equation = 1
Material = 1
Initial Condition = 1
End
Body 2
Name = "heater"
Target Bodies(1) = $heater
Equation = 1
Material = 1
Initial Condition = 2
Body Force = 1
End
Body 3
Name = "fluid"
Target Bodies(1) = $fluid
Equation = 1
Material = 2
Initial Condition = 3
End
Equation 1
Name = "ThermalConduction"
Active Solvers(2) = 1 2
End
Material 1
Name = "Cupper"
Heat Conductivity = 398.0 !! W/m.K
Heat Capacity = 379.0 !! J/kg.K
Reference Temperature = 293.0 !! K
Density = 8.96e+3 !! kg/m3
End
Material 2
Name = "water"
Heat Conductivity = 0.602 !! W/m.K
Heat Capacity = 4.182e3 !! J/kg.K
Reference Temperature = 293.15 !! K
Density = 997.0 !! kg/m3
End
Initial Condition 1
Name = "pipeInitial"
temperature = 293.15
End
Initial Condition 2
Name = "heaterInitial"
temperature = 293.15
End
Initial Condition 3
Name = "fluidInitial"
temperature = 293.15
End
Body Force 1
Name = "HeatSource"
Heat Source = 2.0e3 / 8.96e3
End
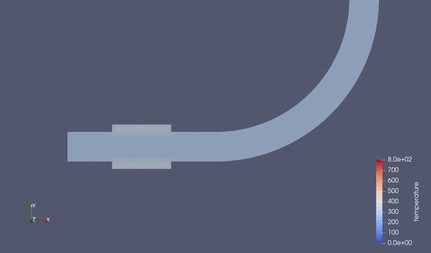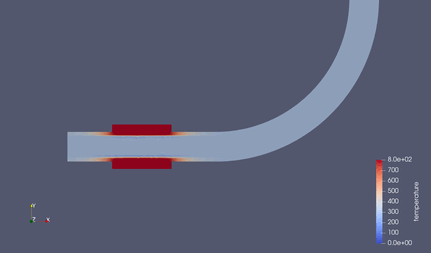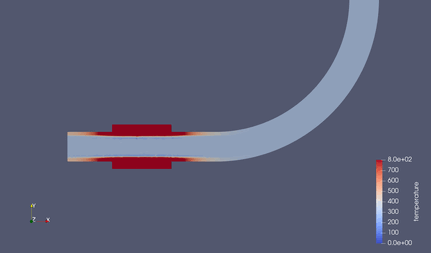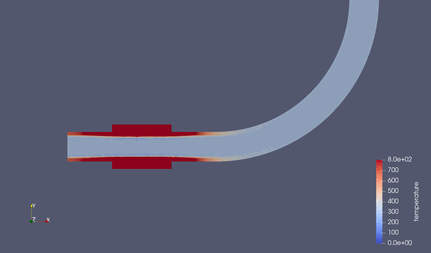
シミュレーション結果¶
結果は以下の通り.
ヒータの熱が時間経過に伴い、パイプ内を伝導していく.
水へはほぼ熱伝導しない.(銅の熱伝導率:398 [W/mk] ⇔ 水の熱伝導率:0.6 [W/mK])
水と銅の比熱差も関係あり. ( 銅の定圧比熱: 379 [J/kgK] ⇔ 水の定圧比熱:4180 [J/kgK] )
実際は、水と銅は比重が10倍弱異なるので、熱容量としてはそこまで大きな差はないが.