直方体中の熱伝導¶
シミュレーション名 :: heatConduction__in_a_bar_XYZ3D
シミュレーション体系¶
基本方程式は熱輸送方程式 ( Heat Equation )
シミュレーション対象は直方体 ( 10 [cm] x 10 [cm] x 100 [cm] )
一端を固定温度条件( 373.15 [K] = 100[℃] )、もう一端は自由境界条件(指定なし)
材質は銅 ( 熱伝導率:398 [W/mK]、 比熱:379 [J/KgK]、8960 [kg/m3] )
メッシュ¶
メッシュ生成スクリプト ( mesh.py )
import numpy as np
import os, sys
import gmsh
import nkGmshRoutines.geometrize__fromTable as gft
import nkGmshRoutines.load__dimtags as ldt
# ========================================================= #
# === 実行部 === #
# ========================================================= #
if ( __name__=="__main__" ):
# ------------------------------------------------- #
# --- [1] initialization of the gmsh --- #
# ------------------------------------------------- #
gmsh.initialize()
gmsh.option.setNumber( "General.Terminal", 1 )
gmsh.option.setNumber( "Mesh.Algorithm" , 5 )
gmsh.option.setNumber( "Mesh.Algorithm3D", 4 )
gmsh.option.setNumber( "Mesh.SubdivisionAlgorithm", 0 )
gmsh.model.add( "model" )
# ------------------------------------------------- #
# --- [2] Modeling --- #
# ------------------------------------------------- #
dimtags = {}
inpFile = "dat/geometry.conf"
dimtags = gft.geometrize__fromTable( inpFile=inpFile )
inpFile = "dat/boundary.json"
dimtags = ldt.load__dimtags( inpFile=inpFile, dimtags=dimtags )
print( dimtags )
gmsh.model.occ.synchronize()
# ------------------------------------------------- #
# --- [3] Mesh settings --- #
# ------------------------------------------------- #
mesh_from_config = True # from nkGMshRoutines/test/mesh.conf, phys.conf
uniform_size = 0.010
if ( mesh_from_config ):
meshFile = "dat/mesh.conf"
physFile = "dat/phys.conf"
import nkGmshRoutines.assign__meshsize as ams
meshes = ams.assign__meshsize( meshFile=meshFile, physFile=physFile, dimtags=dimtags )
else:
import nkGmshRoutines.assign__meshsize as ams
meshes = ams.assign__meshsize( uniform=uniform_size, dimtags=dimtags )
# ------------------------------------------------- #
# --- [4] post process --- #
# ------------------------------------------------- #
gmsh.model.occ.synchronize()
gmsh.model.mesh.generate(3)
gmsh.write( "msh/model.msh" )
gmsh.finalize()
geometry.conf
# <define> @cube.wx = 0.10
# <define> @cube.wy = 0.10
# <define> @cube.wz = 0.50
# <define> @cube.xMin = ( -0.5 ) * @cube.wx
# <define> @cube.yMin = ( -0.5 ) * @cube.wy
# <define> @cube.zMin = 0.0
# <names> key geometry_type centering xc yc zc wx wy wz
cube.01 cube False @cube.xMin @cube.yMin @cube.zMin @cube.wx @cube.wy @cube.wz
boundary.json
{"end.01": [[2, 5]], "end.02": [[2, 6]] }
phys.conf
# <names> key type dimtags_keys physNum
cube.01 volu [cube.01] 301
end.01 surf [end.01] 201
end.02 surf [end.02] 202
mesh.conf
# <names> key physNum meshType resolution1 resolution2 evaluation
cube.01 301 constant 0.010 - -
end.01 201 constant 0.0 - -
end.02 202 constant 0.0 - -
生成したメッシュを次に示す.

Elmer シミュレーションファイル¶
シミュレーションファイル ( ns.sif )を以下に示す.
include "./msh/model/mesh.names"
Header
CHECK KEYWORDS Warn
Mesh DB "." "msh/model"
Include Path ""
Results Directory "out/"
End
Simulation
Max Output Level = 3
Coordinate System = string "Cartesian"
Coordinate Mapping(3) = 1 2 3
Simulation Type = "Transient"
TimeStepping Method = BDF
BDF Order = 2
Timestep sizes(1) = 20.0
Timestep Intervals(1) = 50
Steady State Max Iterations = 1
End
Constants
Stefan Boltzmann = 5.6703e-8 !! -- [ W / m^2 K^4 ] -- !!
End
Solver 1
Equation = "HeatEquations"
Procedure = "HeatSolve" "HeatSolver"
Variable = "Temperature"
Exec Solver = "Always"
Stabilize = True
Bubbles = False
Optimize Bandwidth = True
Steady State Convergence Tolerance = 1.0e-5
Nonlinear System Convergence Tolerance = 1.0e-3
Nonlinear System Max Iterations = 1
Nonlinear System Newton After Iterations = 3
Nonlinear System Newton After Tolerance = 1.0e-3
Nonlinear System Relaxation Factor = 1
Linear System Solver = Iterative
Linear System Iterative Method = BiCGStab
Linear System Max Iterations = 500
Linear System Convergence Tolerance = 1.0e-10
BiCGstabl polynomial degree = 2
Linear System Preconditioning = ILU0
Linear System ILUT Tolerance = 1.0e-3
Linear System Abort Not Converged = False
Linear System Residual Output = 20
Linear System Precondition Recompute = 1
End
Solver 2
Exec Solver = after saving
Equation = "Result output"
Procedure = "ResultOutputSolve" "ResultOutputSolver"
Output File Name = "heat"
Vtu Format = Logical True
Binary Output = Logical True
Scalar Field 1 = String temperature
End
Body 1
Name = "cube"
Target Bodies(1) = $cube.01
Equation = 1
Material = 1
Initial Condition = 1
End
Equation 1
Name = "ThermalConduction"
Active Solvers(2) = 1 2
End
Material 1
Name = "Cupper"
Heat Conductivity = 398.0 !! W/m.K
Heat Capacity = 379.0 !! J/kg.K
Reference Temperature = 293.0 !! K
Density = 8.96e+3 !! kg/m3
End
Initial Condition 1
Name = "cube.initial"
temperature = 293.15 !! = 20 degree
End
Boundary Condition 1
Name = ""
Target Boundaries(1) = $end.01
temperature = 373.15 !! = 100 degree
End
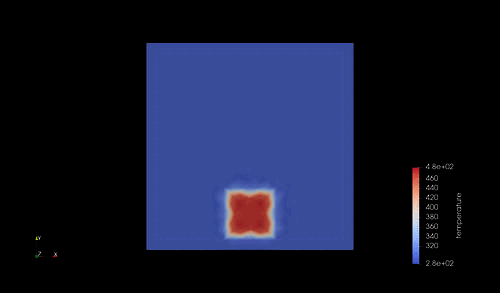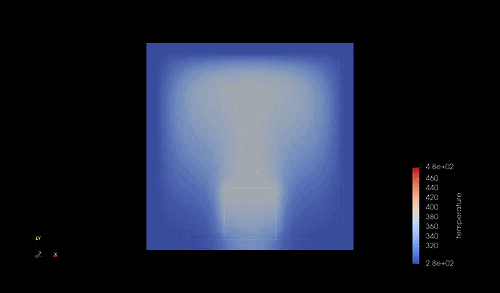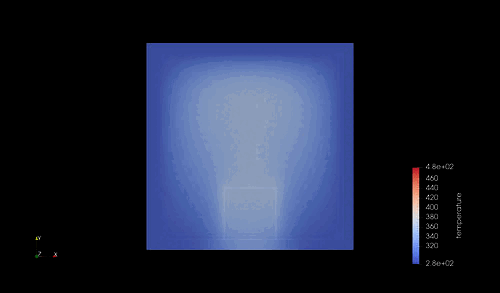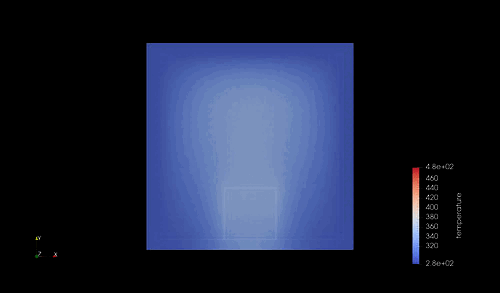
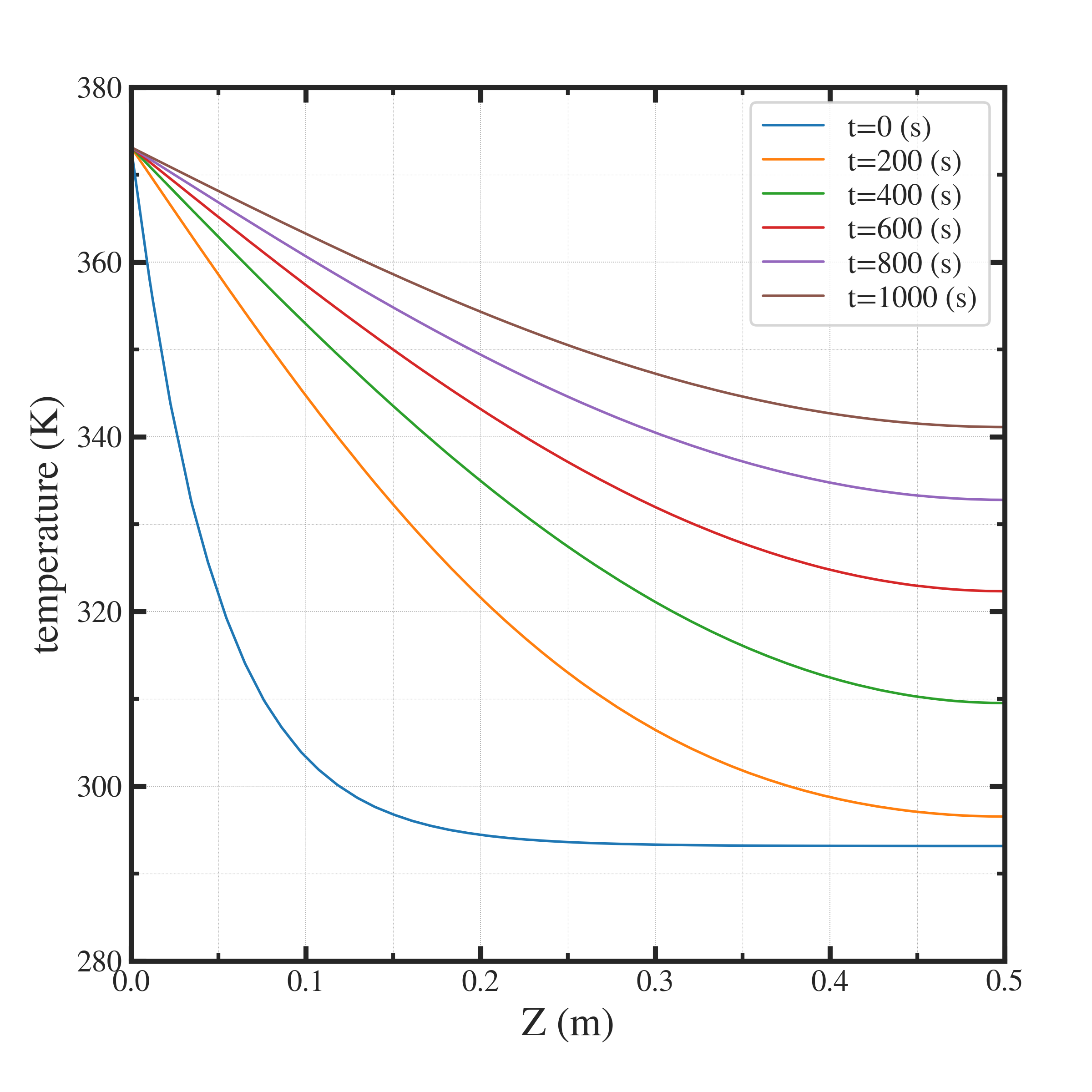
シミュレーション結果¶
結果は以下の通り.
シミュレーションの定量的妥当性¶
シミュレーションで計算した時間は 1000 [s] であり、この間に、自由境界側の一端は 47-48 [K] 程度の温度が上昇している.これが定量的に妥当かどうかを確かめておく.
物性値を以下に示す.
シミュレーションの物性値¶ 物性値
記号
値
単位
長さ
L
0.5
m
断面積
A
0.01
m2
体積
V
0.005
m3
密度 (銅)
ρ
8960
kg/m3
熱伝導率 (銅)
λ
398
W/mK
定圧比熱 (銅)
cp
379
J/kgK
熱伝達の基本式
熱伝導のFourier則は、
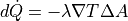
である.これを用いて、熱伝達量は、
![d \dot{Q} = - 398 [W/mK] \times ( 80 [K] / 0.5 [m] ) \times ( 0.1 [m] )^2 = 6.4 \times 10^2 [W/m^2]](../../../_images/math/f0bf00dfaaaf3741bb83b455a5c762a800caa065.png)
である. 100 ℃ のお湯に一端をつけた上記寸法の銅ロッドは、オーブントースター半分程度の熱流束を伝えてくる様子.
シミュレーション時間 1000 [s] 中に伝わる熱量
![Q=640 [W] \times 1000 [s] = 6.4 \times 10^5](../../../_images/math/4df314d60ee4ebb50c0fe4619db8ad219d1395ce.png) が、上昇させる銅の温度
が、上昇させる銅の温度 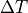 を比熱の式より求めると、
を比熱の式より求めると、![\Delta T &= \dfrac{ \Delta U }{ \rho V c_p } = \dfrac{ 6.4 \times 10^5 }{ 8960 \times 0.005 379 } \\
&= 37.69 [K]](../../../_images/math/edc9b9524093868a9038045a8fd1f156bd96fbdc.png)
となる. 温度勾配を全領域で平均としているなど、かなり大雑把な見積もりであるためか、47-48 ℃ よりも小さい値となっている.実際は、温度勾配は局所的で急峻であり、37.69 [K] よりも高い温度になることが予想される.
概算値とシミュレーションの乖離について¶
例えば、t=0 では、z=0-0.1 [m] の領域において、dT/dz = 700 [K/m] で、計算で用いた 160 [K/m] よりも大きい.
例えば、t=1000 では、 z=0-0.5 [m] の領域において、150 [K/m] 程度である.計算で用いた 160 [K/m] と同程度である.
実際は、時々刻々と変化する温度分布のもとで、温度勾配から熱流束を評価する必要がある(FEM計算の中身).
