線電流が作る磁場¶
直線電流が作る磁場の解析結果を以下に示す. 問題設定、及び、Elmer入力ファイルは、Elmer のテスト問題を参考にしている.
問題設定 / メッシュ¶
半径
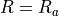 の円筒状導線を一様に流れる直流電流が作る磁場を考える.
の円筒状導線を一様に流れる直流電流が作る磁場を考える.計算領域は、円筒の計算空間を考え、とある半径
 で電磁ポテンシャルは Dirichlet 条件を課す.
で電磁ポテンシャルは Dirichlet 条件を課す.電流として、理想電流 1.0 A を与える.
線電流モデルのメッシュ生成用 gmsh-API python プログラム¶
gmsh-API pythonを利用した片持ち梁モデルの生成プログラム. 自分で作成した箱生成用関数を内部で利用している.
線電流モデルのメッシュ生成用 gmsh-API python プログラム¶
1import numpy as np
2import os, sys
3import gmsh
4
5gmshlib = os.environ["gmshLibraryPath"]
6sys.path.append( gmshlib )
7import generate__quadShape as qua
8import generate__cylinder as cyl
9
10# ------------------------------------------------- #
11# --- [1] initialization of the gmsh --- #
12# ------------------------------------------------- #
13gmsh.initialize()
14gmsh.option.setNumber( "General.Terminal", 1 )
15gmsh.model.add( "model" )
16
17# ------------------------------------------------- #
18# --- [2] initialize settings --- #
19# ------------------------------------------------- #
20ptsDim , lineDim , surfDim , voluDim = 0, 1, 2, 3
21pts , line , surf , volu = {}, {}, {}, {}
22ptsPhys, linePhys, surfPhys, voluPhys = {}, {}, {}, {}
23lc = 0.2
24x_, y_, z_, lc_, tag_ = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
25
26# ------------------------------------------------- #
27# --- [3] Modeling --- #
28# ------------------------------------------------- #
29
30zLeng = 5.0
31wire_r = 0.3
32sim__r = 3.0
33
34xc = [ 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 ]
35delta = [ 0.0, 0.0, zLeng ]
36
37lc_sim = 0.50
38lc_wire = 0.05
39
40ret = cyl.generate__cylinder ( lc=lc_sim, xc=xc, radius=sim__r, \
41 defineVolu=True, extrude_delta=delta )
42volu["Air"] = ret["volu"]["cylinder"]
43
44ret = cyl.generate__cylinder ( lc=lc_wire, xc=xc, radius=wire_r, \
45 defineVolu=True, extrude_delta=delta )
46volu["wire"] = ret["volu"]["cylinder"]
47gmsh.model.occ.removeAllDuplicates()
48
49volu["wire"] = 2
50volu["Air"] = 3
51
52surf["wireIn"] = 4
53surf["wireOut"] = 6
54surf["wireSide"] = 5
55surf["AirIn"] = 8
56surf["AirOut"] = 9
57surf["AirSide"] = 7
58
59# ------------------------------------------------- #
60# --- [4] Physical Grouping --- #
61# ------------------------------------------------- #
62gmsh.model.occ.synchronize()
63surfPhys["wireIn"] = gmsh.model.addPhysicalGroup( surfDim, [ surf["wireIn"] ] , tag=201 )
64surfPhys["wireSide"] = gmsh.model.addPhysicalGroup( surfDim, [ surf["wireSide"] ], tag=202 )
65surfPhys["wireOut"] = gmsh.model.addPhysicalGroup( surfDim, [ surf["wireOut"] ] , tag=203 )
66surfPhys["AirIn"] = gmsh.model.addPhysicalGroup( surfDim, [ surf["AirIn"] ] , tag=204 )
67surfPhys["AirSide"] = gmsh.model.addPhysicalGroup( surfDim, [ surf["AirSide"] ] , tag=205 )
68surfPhys["AirOut"] = gmsh.model.addPhysicalGroup( surfDim, [ surf["AirOut"] ] , tag=206 )
69
70voluPhys["wire"] = gmsh.model.addPhysicalGroup( voluDim, [ volu["wire"] ] , tag=301 )
71voluPhys["Air"] = gmsh.model.addPhysicalGroup( voluDim, [ volu["Air"] ] , tag=302 )
72
73
74# ------------------------------------------------- #
75# --- [2] post process --- #
76# ------------------------------------------------- #
77gmsh.model.occ.synchronize()
78gmsh.model.mesh.generate(3)
79gmsh.write( "model.geo_unrolled" )
80gmsh.write( "model.msh" )
81gmsh.finalize()
82
生成用プログラムの実行は、以下の通り.
モデル生成¶
$ cd msh/
$ python model.py
$ ElmerGrid 14 2 model.msh
$ cd ../
$ mv msh/model ./
ElmerGridによって、( 14 : gmshの.mshファイル、 2 : ElmerMeshファイル4つを含んだディレクトリ )へと変換している.model.header / model.element / model.node / model.boundary が生成される.
線電流が作る磁場のElmer入力ファイル¶
以下にElmer入力ファイルのサンプルを示す.
線電流がつくる磁場の Elmer 入力ファイル ( line_current.sif )¶
1
2CHECK KEYWORDS "Warn"
3
4Header
5 Mesh DB "." "model"
6 Include Path ""
7 Results Directory ""
8End
9
10Simulation
11 coordinate system = "Cartesian"
12
13 Simulation Type = "Steady State"
14 Steady State Max Iterations = 1
15
16 Solver Input File = "line_current.sif"
17 Output File = "results/line_current.dat"
18 Post File = "line_current.vtu"
19End
20
21
22Constants
23End
24
25Body 1
26 Target Bodies(1) = 301
27 Name = "Conductor"
28
29 Equation = 1
30 Material = 1
31 Body Force = 1
32End
33
34Body 2
35 Target Bodies(1) = 302
36 Name = "Air"
37
38 Equation = 1
39 Material = 2
40End
41
42
43Material 1
44 Name = "Conductor"
45 Relative Permittivity = 1.0
46 Relative Permeability = 1.0
47 Electric Conductivity = 5.80e7
48End
49
50Material 2
51 Name = "Air"
52 Relative Permittivity = 1.0
53 Relative Permeability = 1.0
54 Electric Conductivity = 0.0
55End
56
57
58Equation 1
59 Name = "Magnetic Field Equations for Conductor"
60 Active Solvers(3) = 1 2 3
61End
62
63
64Equation 2
65 Name = "Magnetic Field Equations for Air"
66 Active Solvers(2) = 2 3
67End
68
69
70Solver 1
71 Equation = "CoilSolver"
72 Procedure = "CoilSolver" "CoilSolver"
73
74 Linear System Solver = "Iterative"
75 Linear System Preconditioning = "ILU1"
76 Linear System Max Iterations = 1000
77 Linear System Convergence Tolerance = 1e-10
78 Linear System Iterative Method = BiCGStabL
79 Linear System Residual Output = 20
80 Steady State Convergence Tolerance = 1e-06
81
82 Desired Coil Current = Real 1.0
83 Nonlinear System Consistent Norm = True
84End
85
86Solver 2
87 Equation = "AV"
88 Procedure = "MagnetoDynamics" "WhitneyAVSolver"
89
90 Linear System Symmetric = True
91 Linear System Solver = "Iterative"
92 Linear System Preconditioning = None
93 Linear System Residual Output = 10
94 Linear System Max Iterations = 1000
95 Linear System Iterative Method = GCR
96 Linear System Convergence Tolerance = 1.0e-8
97 BicgStabl Polynomial Degree = 4
98End
99
100Solver 3
101 Equation = "MGDynamicsCalc"
102
103 Procedure = "MagnetoDynamics" "MagnetoDynamicsCalcFields"
104 Linear System Symmetric = True
105
106 Potential Variable = String "AV"
107
108 Calculate Current Density = Logical True
109 Calculate Electric Field = Logical True
110 Calculate Magnetic Field Strength = Logical True
111 Calculate Joule Heating = True
112
113 Steady State Convergence Tolerance = 0
114 Linear System Solver = "Iterative"
115 Linear System Preconditioning = None
116 Linear System Residual Output = 0
117 Linear System Max Iterations = 5000
118 Linear System Iterative Method = CG
119 Linear System Convergence Tolerance = 1.0e-8
120
121 Calculate Nodal Fields = Logical False
122 Impose Body Force Potential = Logical True
123 Impose Body Force Current = Logical True
124 Discontinuous Bodies = True
125End
126
127Solver 4
128 Exec Solver = after all
129 Equation = "ResultOutput"
130 Procedure = "ResultOutputSolve" "ResultOutputSolver"
131 Output File Name = wire
132 Vtu format = Logical True
133 Discontinuous Bodies = Logical True
134End
135
136Solver 5
137 Exec Solver = after all
138 Equation = "SaveLine"
139 Procedure = "SaveData" "SaveLine"
140 FileName = "bfield_inline.dat"
141
142 Polyline Coordinates(2,3) = -5.0e-3 0.0 5.0e-3 5.0e-3 0.0 5.0e-3
143 Polyline Divisions(1) = 100
144End
145
146
147Body Force 1
148! a) Give current density
149! Current Density 1 = Equals "CoilCurrent 1"
150! Current Density 2 = Equals "CoilCurrent 2"
151! Current Density 3 = Equals "CoilCurrent 3"
152
153! b) Give the driving external potential
154 Electric Potential = Equals "CoilPot"
155End
156
157
158Boundary Condition 1
159 Name = "WireStart"
160 Target Boundaries(1) = 201
161 Coil Start = Logical True
162 AV {e} 1 = Real 0.0
163 AV {e} 2 = Real 0.0
164 AV = Real 0.0
165End
166
167Boundary Condition 2
168 Name = "WireSurface"
169 Target Boundaries(1) = 202
170End
171
172Boundary Condition 3
173 Name = "WireEnd"
174 Target Boundaries(1) = 203
175 Coil End = Logical True
176 AV {e} 1 = Real 0.0
177 AV {e} 2 = Real 0.0
178 AV = Real 0.0
179End
180
181Boundary Condition 4
182 Name = "AirStart"
183 Target Boundaries(1) = 204
184 AV {e} 1 = Real 0.0
185 AV {e} 2 = Real 0.0
186End
187
188
189Boundary Condition 5
190 Name = "AirSurface"
191 Target Boundaries(1) = 205
192 AV {e} 1 = Real 0.0
193 AV {e} 2 = Real 0.0
194End
195
196Boundary Condition 6
197 Name = "AirEnd"
198 Target Boundaries(1) = 206
199 AV {e} 1 = Real 0.0
200 AV {e} 2 = Real 0.0
201End
202
線電流がつくる磁場の解析結果¶
解析実行結果は以下に示す.以下に電流密度分布と磁界強度を示す.
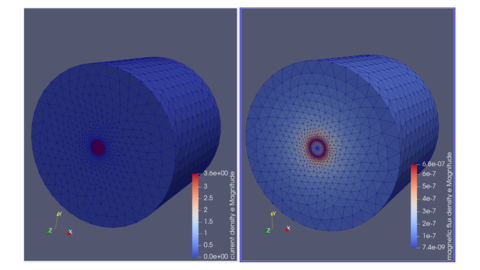
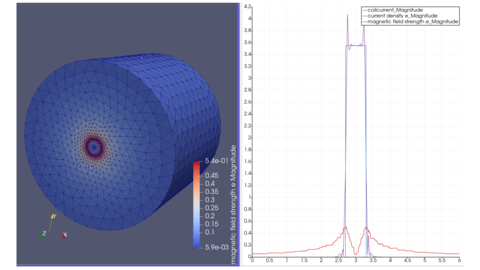
以下に磁束密度分布と磁場・電流の径方向1次元分布を示す.
線電流がつくる磁場は、Ampere則、
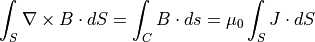
を用いて解析的に計算できる.まずは、導体中の磁束密度は、
![2 \pi r B &= \mu_0 J \int_0^r 2 \pi r^{\prime} dr^{\prime} = 2 \pi \mu_0 J [ \dfrac{1}{2}r^{\prime 2 } ]^r_0 \\
B(r) &= \dfrac{ \mu_0 J r }{ 2 }](../../../_images/math/53d5a3723060d01287bc68b2134b7947eeac6098.png)
導体外側空気領域の磁束密度は、
![2 \pi r B &= \mu_0 J \int_0^a 2 \pi r^{\prime} dr^{\prime} = 2 \pi \mu_0 J [ \dfrac{1}{2}r^{\prime 2} ]^a_0 \\
B(r) &= \dfrac{ \mu_0 J a^2 }{ 2 r } = \dfrac{ \mu_0 I }{ 2 \pi r }](../../../_images/math/b784eded1143262c0ca018182a6215e182f56b1c.png)
一次元分布をみると、磁界強度は導体円筒中はrに対して線形に増加し、外側では 1/r で減少しているため、理論解と定性的に一致している.
